Easing Methods
Overview Table -->
Each EasyEase Object comes with a set of functional methods that reproduce the most common easing curves:
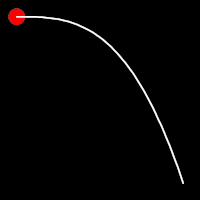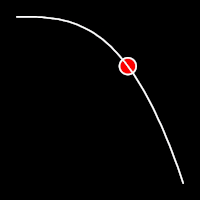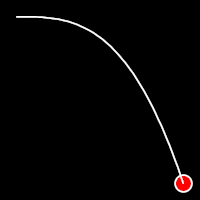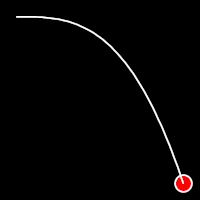
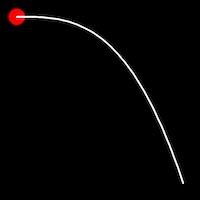
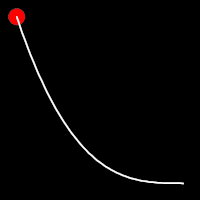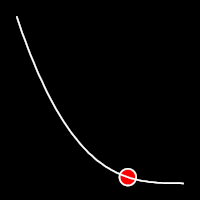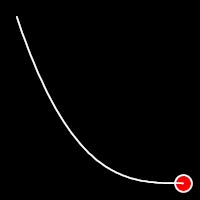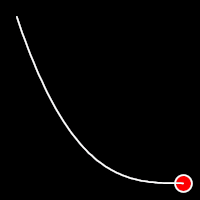
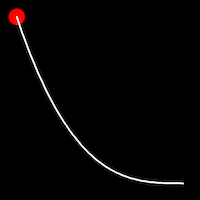
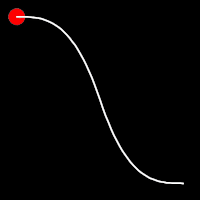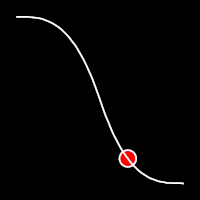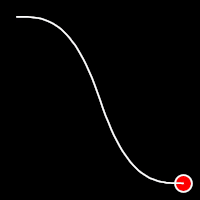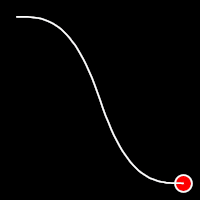
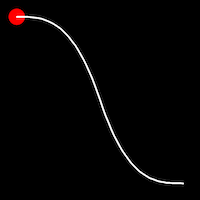
Exponential Easing
Exponential easing accelerates or decelerates motion based on the value of the exponential factor. the higher the factor, the steeper the curve
.in()
It starts slowly and progressively speeds up,
.out()
It starts fast and progressively slows down,
.inOut()
It starts slow, accelerates until reaching full-speed at the midpoint, then and progressively slows down.
| ease - in | ease - out | ease-in-out |
|---|---|---|
Exponential |
||
  |
  |
  |
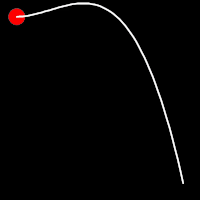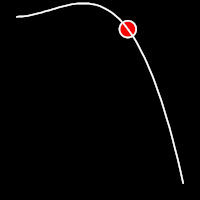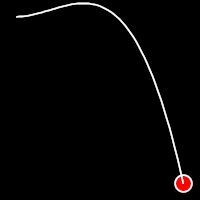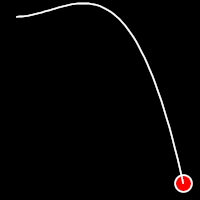
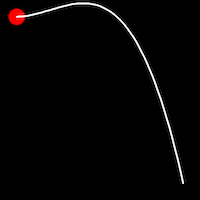
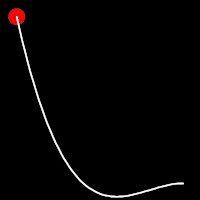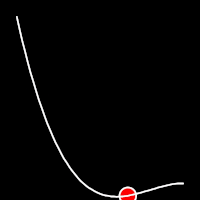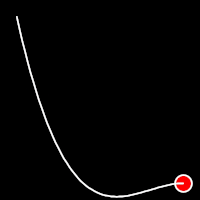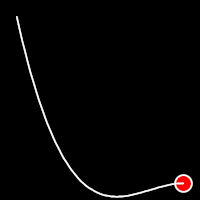
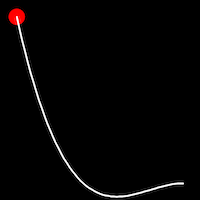
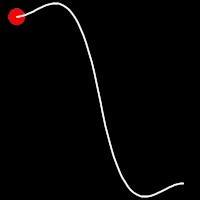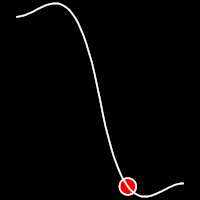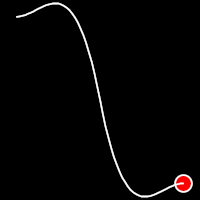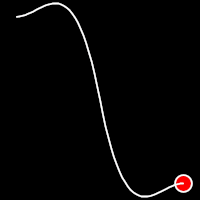
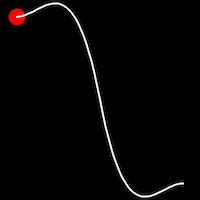
Back Easing
Back easing incorporates a brief overshoot before settling into the target position. This method is characterized by a slight backward motion before moving forward, creating an effect similar to pulling back and releasing a spring.
.inBack()
It starts slowly and progressively speeds up,
.outBack()
It starts slowly and progressively speeds up,
.inOutBack()
It starts slow, accelerates until reaching full-speed at the midpoint, then and progressively slows down.
| ease - in | ease - out | ease-in-out |
|---|---|---|
Back |
||
  |
  |
  |
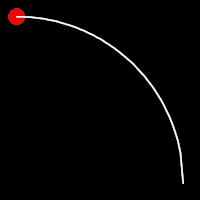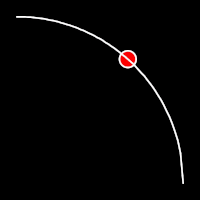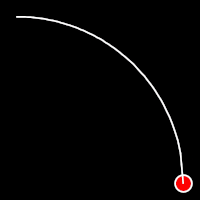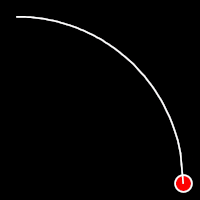
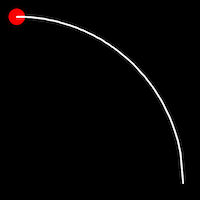
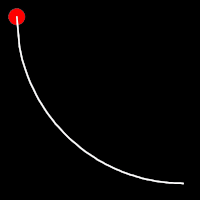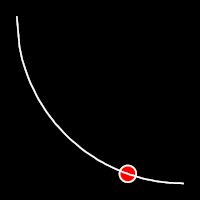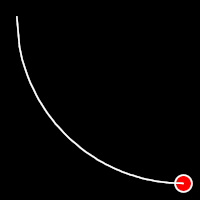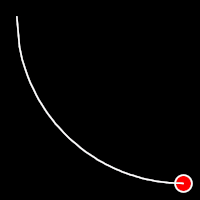
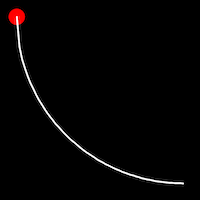
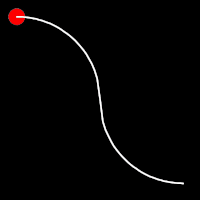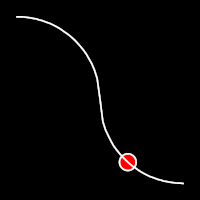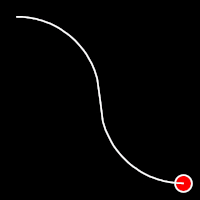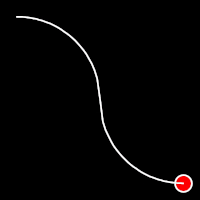
Circular Easing
Circular easing follows a circular motion pattern. This method is characterized by its rounded curves
.inCirc()
It starts slowly and progressively speeds up,
.outCirc()
It starts slowly and progressively speeds up,
.inOutCirc()
It starts slow, accelerates until reaching full-speed at the midpoint, then and progressively slows down.
| ease - in | ease - out | ease-in-out |
|---|---|---|
Circular |
||
  |
  |
 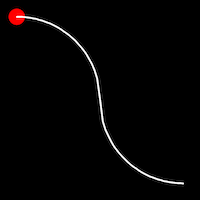 |
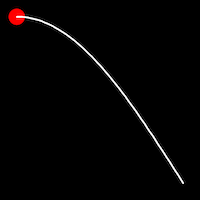
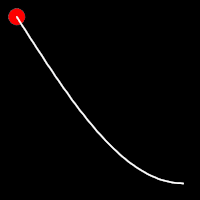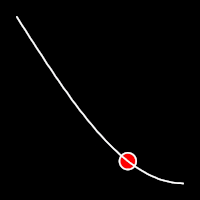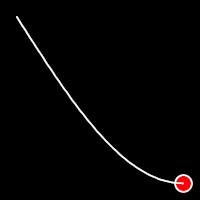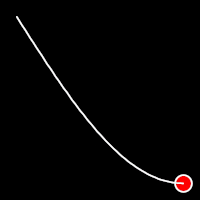
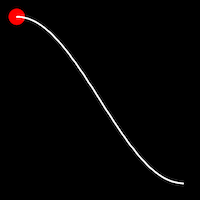
Sinusoidal Easing
Sinusoidal easing applies a sinusoidal function to the motion, resulting in a smooth, wave-like transition, providing a gentle acceleration and deceleration.
.inSine()
It starts slowly and progressively speeds up,
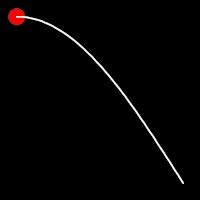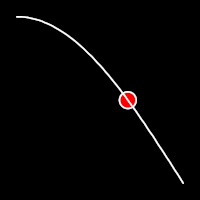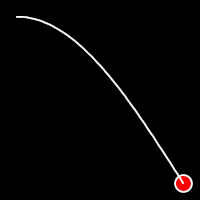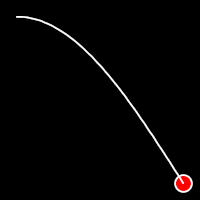
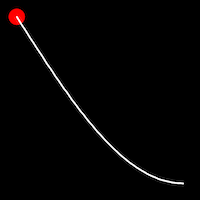
.outSine()
It starts slowly and progressively speeds up,
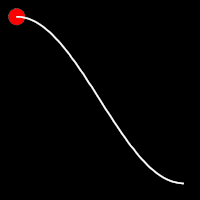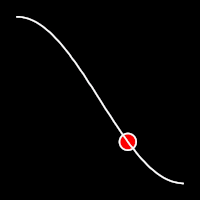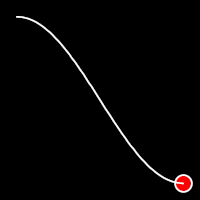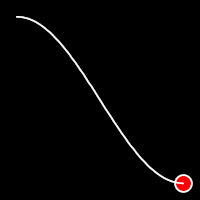
.inOutSine()
It starts slow, accelerates until reaching full-speed at the midpoint, then and progressively slows down.
| ease - in | ease - out | ease-in-out |
|---|---|---|
Sinusoidal |
||
  |
  |
  |
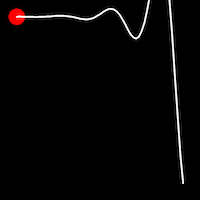
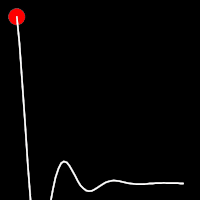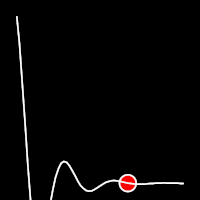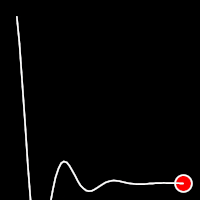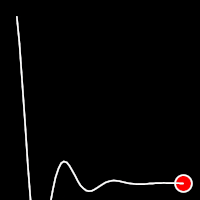
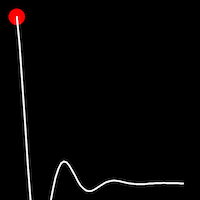
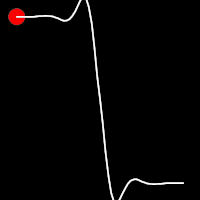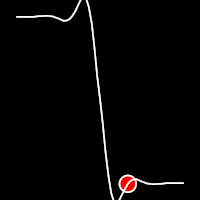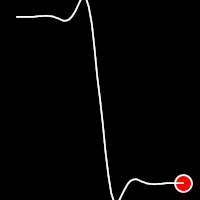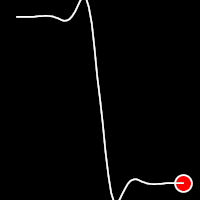
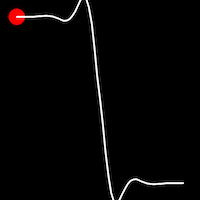
Elastic Easing
Elastic easing simulates an elastic or rubber band-like motion, causing the object to overshoot its target before settling into the final position. This method is useful for creating bouncy animations.
.inElastic()
It starts slowly and progressively speeds up,
.outElastic()
It starts slowly and progressively speeds up,
.inOutElastic()
It starts slow, accelerates until reaching full-speed at the midpoint, then and progressively slows down.
| ease - in | ease - out | ease-in-out |
|---|---|---|
Elastic |
||
  |
  |
  |
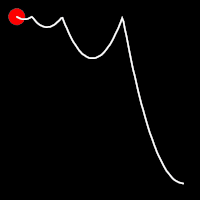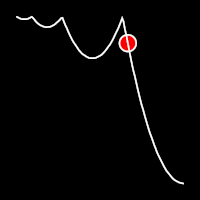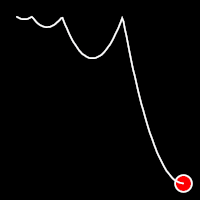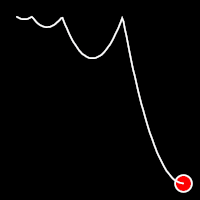
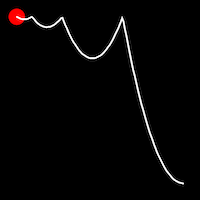
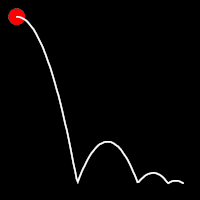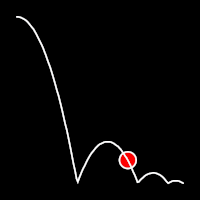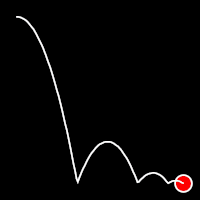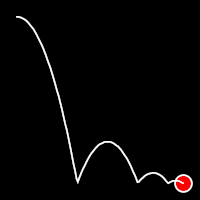
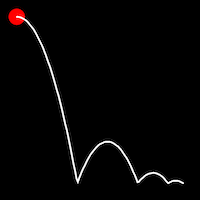
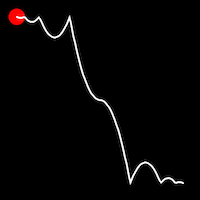
Bounce Easing
Bounce easing mimics the behavior of a bouncing ball, introducing a series of bounces as the motion progresses. This method adds a dynamic animation, resembling the way objects bounce in the real world.
.inBounce()
It starts slowly and progressively speeds up,
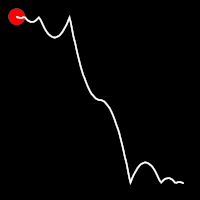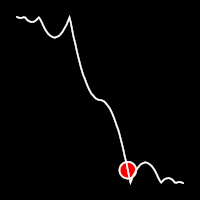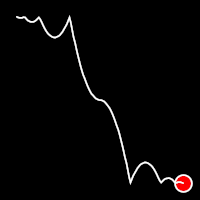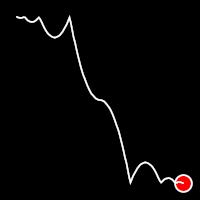
.outBounce()
It starts slowly and progressively speeds up,
.inOutBounce()
It starts slow, accelerates until reaching full-speed at the midpoint, then and progressively slows down.
| ease - in | ease - out | ease-in-out |
|---|---|---|
Bounce |
||
  |
  |
  |